To understand more on this topic, check out our unit price calculator and cost of goods sold calculator. Direct materials quantity variance is a part of the overall materials cost variance that occurs due to the difference between the actual quantity of direct materials used and the standard quantity allowed for the output. If the actual purchase price is higher than the standard price, we say that the direct material price variance is adverse or unfavorable. This is because the purchase of raw materials during the period would have cost the business more than what was allowed in the budget.
Formula(s) to Calculate Direct Material Price Variance
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Meanwhile, actual cost comes from real bills and receipts showing what your company did pay. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications.
Material Price Variance Calculator
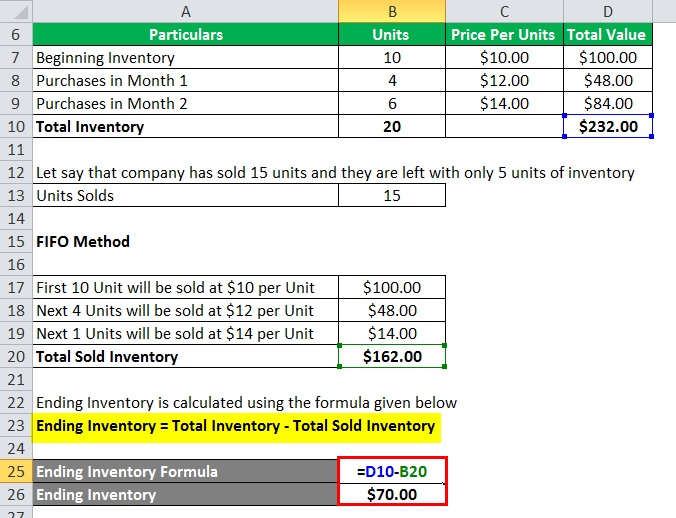
Understanding direct material variance is crucial for businesses aiming to maintain cost efficiency and improve profitability. This concept involves examining the differences between expected and actual costs of materials used in production, providing insights into potential areas for financial improvement. To apply this method to the Band Book example, take a look at the next diagram. Direct materials actually cost $297,000, even though the standard cost of the direct materials is only $289,800.

Do you already work with a financial advisor?
- It also shows that the actual price per pound was $0.30 higher than standard cost (unfavorable).
- A favorable materials quantity variance indicates savings in the use of direct materials.
- These reports should be detailed and timely, allowing managers to quickly identify and address any discrepancies.
Understanding the mechanism behind material price variance is fundamental in managerial accounting, serving as a tool to control costs and pinpoint discrepancies. This measures how much a company’s actual spending on materials differs from its expected spending. Think of it as checking if you paid more or less for materials than planned. Technological advancements and automation also influence direct material variance. The integration of advanced technologies, such as IoT and AI, into the production process can provide real-time data on material usage and identify inefficiencies.
Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own.
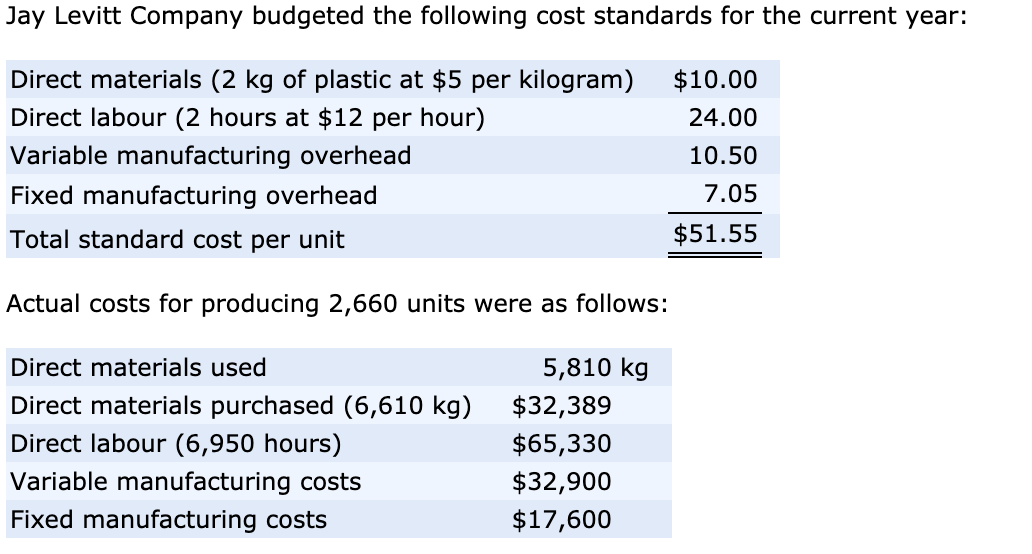
The direct materials price variance of Hampton Appliance Company is unfavorable for the month of January. This is because the actual price paid to buy 5,000 units of direct material exceeds the standard price. The direct material price variance is the difference between the actual price paid to acquire a direct materials item and its budgeted price, multiplied by the actual number of units acquired. This information is needed to monitor the costs incurred to produce goods.
Direct material price variance (DM Price Variance) is defined as the difference between the expected and actual cost incurred on purchasing direct materials. It evaluates the extent to which the standard price has been how to apply for a colorado sales tax license over or under applied to different units of purchase. With our direct material price variance calculator, we aim to help you assess the difference between the actual cost of direct materials and the standard cost.
Understanding the factors that influence direct material variance is essential for businesses aiming to maintain control over their production costs. Market conditions, geopolitical events, and changes in supply and demand can all cause fluctuations in material costs. For instance, a sudden increase in the price of steel due to international trade policies can lead to an unfavorable material price variance for manufacturers relying on this resource. Companies must stay informed about market trends and consider strategies such as hedging or long-term contracts to mitigate these risks.
This ensures that the entire gain or loss on the procurement of materials is reflected in the results of the current period. Evaluating material price variance is pivotal for a business, as it sheds light on the efficiency of purchasing activities and can signal areas for financial improvement. By honing in on this metric, organizations unlock insights into whether deviations from standard costs are working to their advantage or pointing to underlying issues in procurement processes. This step is where you find out if you spent more or less than planned on materials. You calculate this price difference by subtracting the actual cost from the standard cost for each unit bought.