Unlike the cash ratio and quick ratio, it does not exclude any component of the current assets. The current ratio evaluates the capacity of a company to pay its debt obligations using all of its current assets. Inventory items are considered current assets when a business plans to sell them for profit within twelve months. Assets are on the top of a balance sheet, and below them are the company’s states with the highest sales tax rates in the usa liabilities, and below that is shareholders’ equity. A balance sheet is also always in balance, where the value of the assets equals the combined value of the liabilities and shareholders’ equity. This means that assets, or the means used to operate the company, are balanced by a company’s financial obligations, along with the equity investment brought into the company and its retained earnings.
Current (Short-Term) Liabilities

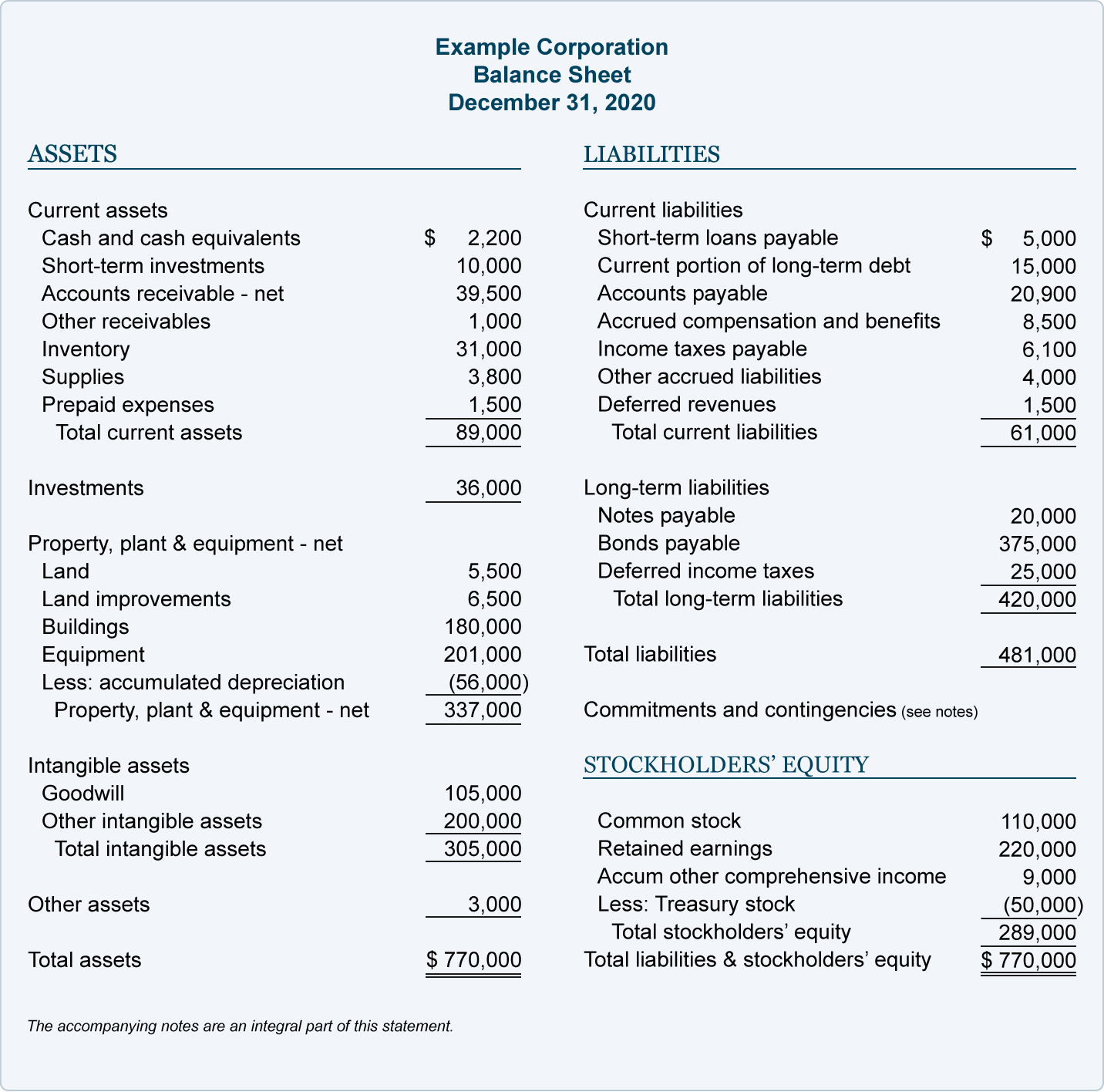
Liabilities and equity make up the right side of the balance sheet and cover the financial side of the company. With liabilities, this is obvious—you owe loans to a bank, or repayment of bonds to holders of debt. Liabilities are listed at the top of the balance sheet because, in case of bankruptcy, they are paid back first before any other funds are given out. A balance sheet is one of the primary statements used to determine the net worth of a company and get a quick overview of its financial health.
Balance Sheet Formats
Current assets include, but are not limited to, cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable, and inventory. Their cost will be depreciated on the financial statements over their useful lives. The purpose of a balance sheet is to give interested parties an idea of the company’s financial position, in addition to displaying what the company owns and owes. It is important that all investors know how to use, analyze and read a balance sheet. Current liabilities are the company’s liabilities that will come due, or must be paid, within one year.
Current Assets vs. Noncurrent Assets
The reported amount on the retailer’s balance sheet is the cost of merchandise that was purchased, but not yet sold to customers. What is the proper amount of cash a company should keep on its balance sheet? A bank statement is often used by parties outside of a company to gauge the company’s health.
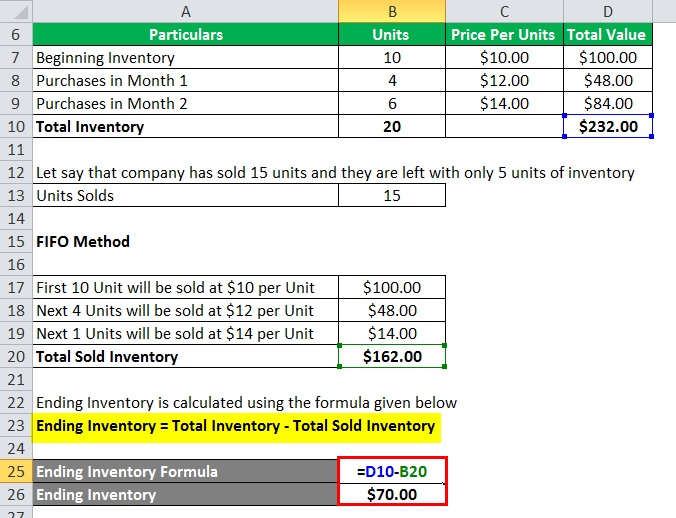
What is the formula to calculate current assets?
It would be classified as a noncurrent asset if it is a long-term investment, such as a bond. A low cash ratio is not necessarily bad because there might be situations that skew the balance sheets of a company. Similar to the example shown above, if the cash ratio is 1 or more, the company can easily meet its current liabilities at any time. Current assets play a big role in determining some of these ratios, such as the current ratio, cash ratio, and quick ratio.
- Current assets play a big role in determining some of these ratios, such as the current ratio, cash ratio, and quick ratio.
- They are grouped as current liabilities and long-term liabilities in the balance sheet.
- Assets are what the company owns, while liabilities are what the company owes.
- They are divided into current assets, which can be converted to cash in one year or less; and non-current or long-term assets, which cannot.
- The line buildings and improvements reports the cost of the buildings and improvements but not the cost of the land on which they were constructed.
Should all of its current liabilities suddenly become due, the value of its current assets would not be enough to cover the needed payments. A negative working capital, on the other hand, means that the company does not have enough current assets to pay its current liabilities. Then, when the benefits of these assets are realized over time, the amount is then recorded as an expense. Inventory is considered more liquid than other assets, such as land and equipment but less liquid than other short-term investments, like cash and cash equivalents. This is the most liquid form of current asset, which includes cash on hand, as well as checking or savings accounts. The noncurrent balance sheet item other assets reports the company’s deferred costs which will be charged to expense more than a year after the balance sheet date.
After you have assets and liabilities, calculating shareholders’ equity is done by taking the total value of assets and subtracting the total value of liabilities. This may include accounts payables, rent and utility payments, current debts or notes payables, current portion of long-term debt, and other accrued expenses. It is also possible to grasp the information found in a balance sheet to calculate important company metrics, such as profitability, liquidity, and debt-to-equity ratio.
Balance sheets are typically prepared at the end of set periods (e.g., annually, every quarter). Public companies are required to have a periodic financial statement available to the public. That is why there is no need to have their financial statements published to the public.
For instance, accounts receivable should be continually assessed for impairment and adjusted to reveal potential uncollectible accounts. Again, these should be organized into both line items and total liabilities. If the company wanted to, it could pay out all of that money to its shareholders through dividends. Assets are anything the company owns that holds some quantifiable value, which means that they could be liquidated and turned into cash.