This ongoing log of records allows the details of your business’s financial records to be tracked. These details are then used to build up your financial statements to show how much you own and owe (balance sheet) and how much you are earning or losing (income statements). With your financial statements and financial data accurate and complete, you will be able to perform analysis and make impactful business decisions. Any time you sell a product or service, your accounting books must be updated to reflect each transaction. When this is done, the proper transaction gets recorded into the accounts. And when your business purchases products or services from other companies or business entities, you also need to use the accounts to keep track of such transactions.
Real Accounts
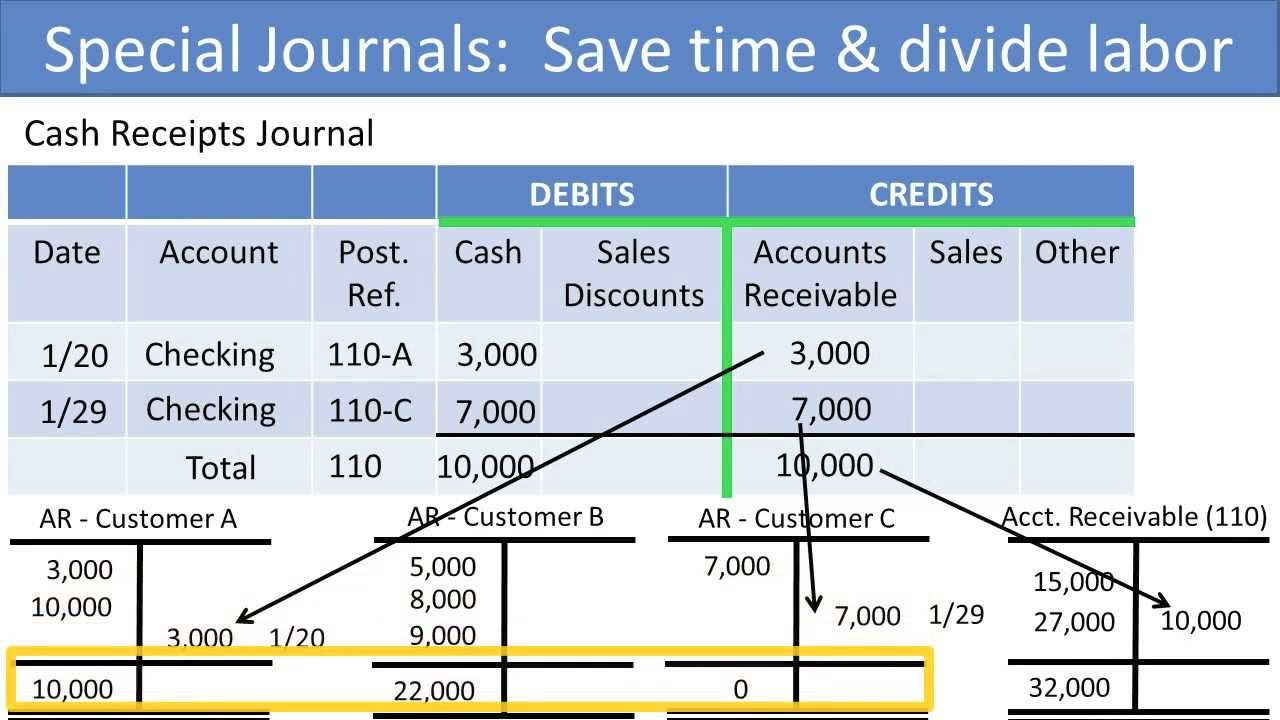
Say you make a $200 sale to a customer who pays with credit. Through the sale, you increase your Revenue account through a credit. And, increase your Accounts Receivable account through a debit. Equity is the difference between your assets and liabilities. Sub-accounts show you exactly where funds are coming in and out of. And, you can better track how much money you have in each individual account.
Posting to the Accounting Ledger
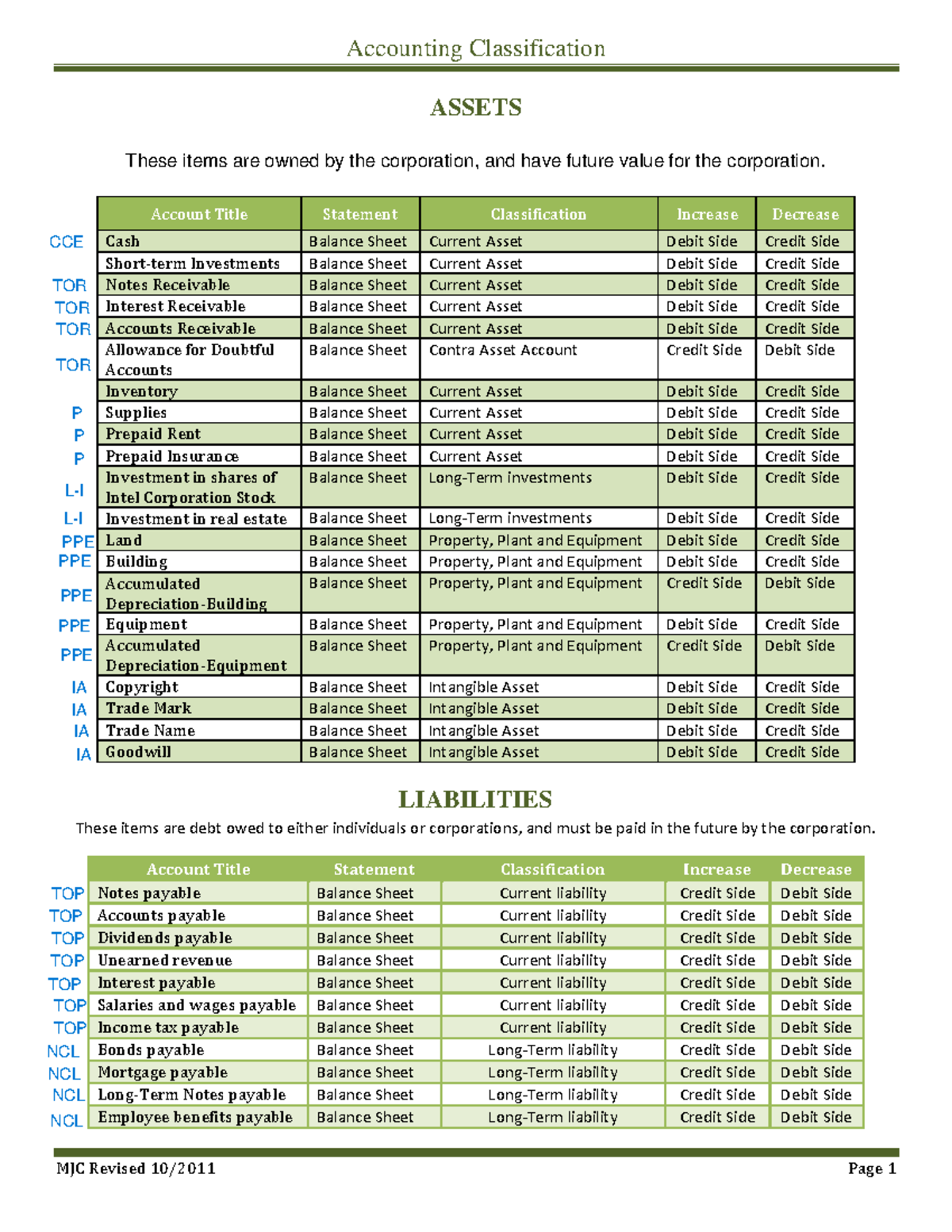
- Due to its more holistic approach, the modern classification of accounts (assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses & capital) has gained more followers than the traditional classification (real, personal & nominal).
- Revenue accounts are critical to any business, and ensuring you are tracking your transactions accurately will give you real-time information on how your business is growing.
- This article provides an overview of the various types of accounts in accounting and their significance, particularly in the Indian context.
- The list of transactions in a particular account is called a ledger.
Let’s say that you sell $1000 worth of your inventory, money which you then place into your bank account. You would then simply increase (debit side) your bank account by $1000 and decrease (credit side) your Inventory account. By carefully tracking the transaction into its respective accounts, you’ll be able to keep track of all types of intangible and tangible assets—in this case, both your inventory and your revenue.
Equity Accounts
Accounts Payable – purchased assets by placing on an account from a supplier that we will pay in the future. The cost of producing or purchasing the goods sold by the company. This includes raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overheads. Note that in accounting we usually show negative numbers in parenthesis instead of with a minus sign.
FAQs on Types of Accounts in Accounting
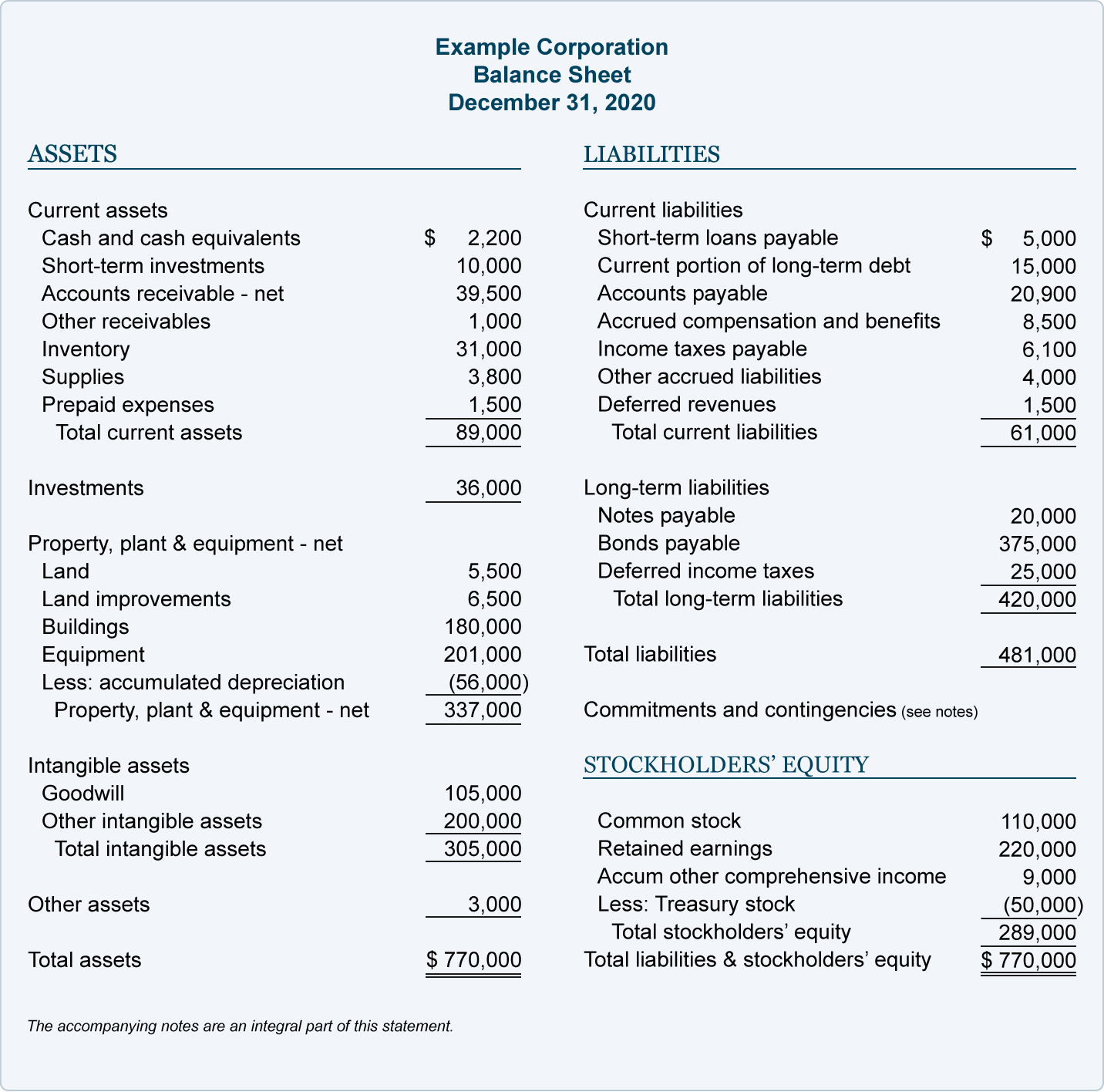
By doing this, all financial events of a business are accurately recorded and accounted for. As a result, in the light of the accounting equation, debits are always equal to credits and the balance sheet is always a match. Different types of financial statements are created using transactional information from accounts. A company’s financial position, operational performance, etc., are all represented using the same data. Permanent in nature, real accounts are carried from one accounting period to the next without being revalued.
On the other hand, asset accounts keep track of items and other things of value—from credits owed to you to the funds in your bank account—that can provide economic gains for your company. For example, there could be one account called Travel Expenses, but with sub-accounts like Travel Meals and Flight to track the travel expenses in more detailed categories. You can easily report on the most applicable sub-account to get a sense of the financials in that category.
Accounts which are related to expenses, losses, incomes or gains are called Nominal accounts. Now that you know how accounts and sub-accounts work, you can make the necessary adjustments to your company’s bookkeeping. In doing so, you can effectively record and monitor to reduce unnecessary spending, increase revenue, and meet financial goals. Revenue accounts are critical to any business, and ensuring you are tracking your transactions accurately will give you real-time information on how your business is growing.
Having explicit knowledge about it can help you cover the whole section. Personal accounts created by law are called artificial personal accounts. Example – Purchases, Sales, Salaries, Commission Received, Bad Debts, Telephone Bills, etc. The final result of all nominal accounts is either profit or loss which is then transferred to the capital account.
Apart from the executive teams, some supervisors continuously observe the process. For running any business smoothly and efficiently one should maintain accounts. Accounting helps you to track income and expenditures and provides investors, administration, and government with quantitative financial information which can be used in making business. Both classifications are used in accounting, depending on the context and preference of the organization. Representative personal accounts represent a certain person or a group.
The classification of accounts is an essential part of bookkeeping and financial reporting. By understanding the different categories of accounts, businesses can effectively organize and like-kind exchange analyze their financial information, make informed decisions, and maintain financial stability. Keeping track of your different types of accounts in accounting can be a challenge.
Modified cash-basis and accrual accounting use the same accounts, which are advanced accounts such as AP and long-term liabilities. Now that we have a basic understanding of accounts, we can analyze and record transactions through the accounting cycle. Some other data are extracted through mathematics and the information of the future data. These are all done following the statistical processes to make a final financial-accounting report of the company. All these processes should be executed in the correct order to get the best outcome in the form of computer-driven data.